Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) lung infection
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) infection is common (over 80% of infants will have been infected with RSV by the age of two). In most cases this is a mild upper respiratory tract infection but can lead to hospitalization in approximately 30 % of babies (< 6 months old) and 10 % of those aged over 65. It is the largest cause of bronchiolitis.
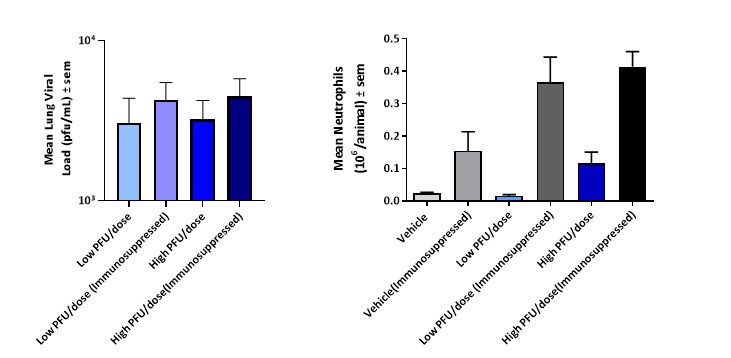
A mild disease state can be induced in both immunocompromised and non-immunocompromised mice with recoverable levels of RSV form the lung and increased inflammatory cells.
For the assessment of antivirals we have an on-site microbiology Department who will prepare, assess the viral dose and can assess viral load in the lung tissue.
| Study Design | |
|---|---|
| Species/Strain | Balb/c mouse (immunocompromised) |
| Model | RSV lung infection model |
| Relevant Use | Screening and assessment of new anti-viral and anti-inflammatory drugs for viral respiratory disease |
| Readouts Available | Daily Bodyweights and Clinical Signs, Lung Function (penH, Resistance, Compliance, FEV), Viral load, BAL differential cell counts, BAL cytokines and Pathology |
Study data generated by Labcorp Huntingdon Pharmacology.
Related Models
-
Bhas 42 Cell Transformation Assay (CTA)
Carcinogenicity, Discovery, Toxicology -
Monocrotaline induced Pulmonary Hypertension (PAH)
Discovery -
Asthma: Ovalbumin sensitization and challenge
Discovery -
Chlorine Induced Lung Injury
Discovery -
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) neutropenic thigh infection model
Discovery -
COPD: LPS + fMLP PK/PD model – Neutrophil Elastase Targets
Discovery -
COPD: Human Neutrophil Elastase Lung Hemorrhage Model
Discovery -
Bronchoconstriction models for LABA, LAMA & MABAs
Discovery
